سدیم بوروهیدرید|سدیم تترا هیدروبورات
سدیم بوروهیدرید یا بوروهیدرید سدیم
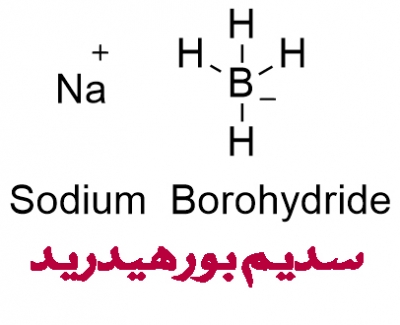
سدیم بوروهیدرید یا بوروهیدرید سدیم که با نامهای تتراهیدریدوبورات سدیم و تتراهیدروبورات سدیم همچنین سدیم تترا هیدروبورات نیز شناخته میشود، یک ترکیب معدنی با فرمول NaBH4 است.
سدیم بوروهیدرید به صورت پودر و جامد سفید رنگ و بی بو می باشد .
ویژگیهای سدیم بوروهیدرید
سدیم بوروهیدرید یک عامل کاهنده است که هم در آزمایشگاه و هم در مقیاس صنعتی در شیمی کاربرد دارد. این به عنوان پیش تصفیه برای خمیرسازی چوب آزمایش شده است، اما برای تجاری سازی آن بسیار پرهزینه است.
این ترکیب در الکلها، اترهای خاص و آب محلول است، اگرچه به آرامی هیدرولیز میشود.
NaBH4 بسیاری از کربونیل های آلی را بسته به شرایط دقیق کاهش می دهد. معمولاً در آزمایشگاه برای تبدیل کتون ها و آلدئیدها به الکل استفاده می شود.
کلریدهای آسیل، انیدریدها، a-هیدروکسیلاکتون ها، تیواسترها و ایمین ها را در دمای اتاق یا کمتر به طور موثر کاهش می دهد. این استرها را به آرامی و به طور ناکارآمد با بیش از حد معرف و/یا دماهای بالا کاهش می دهد، در حالی که اسیدهای کربوکسیلیک و آمیدها به هیچ وجه کاهش نمی یابند.
18 NaBH4 با آب و الکل ها، با تکامل گاز هیدروژن و تشکیل بورات مربوطه واکنش می دهد، که واکنش به ویژه انجام می شود. سریع در PH پایین با این وجود، یک الکل، اغلب متانول یا اتانول، به طور کلی حلال انتخابی برای احیای بوروهیدرید سدیم کتون ها و آلدئیدها است.
مکانیسم احیای کتون و آلدئید توسط مطالعات جنبشی مورد بررسی قرار گرفته است، و برخلاف تصورات رایج در کتابهای درسی، این مکانیسم شامل یک حالت گذار 4 عضوی مانند هیدروبوراسیون آلکن، [19] یا یک حالت گذار شش عضوی شامل یک مولکول نمیشود.
از حلال الکلی. 20 فعال سازی پیوند هیدروژنی مورد نیاز است، زیرا هیچ کاهشی در یک حلال آپروتیک مانند دیگلیم رخ نمی دهد. با این حال، ترتیب نرخ در الکل 1.5 است، در حالی که ترکیب کربونیل و بوروهیدرید هر دو مرتبه اول هستند، که مکانیسمی پیچیدهتر از یک حالت گذار شش عضوی را نشان میدهد که شامل تنها یک مولکول الکل است.
پیشنهاد شد که فعال شدن همزمان ترکیب کربونیل و بوروهیدرید به ترتیب از طریق برهمکنش با الکل و یون آلکوکسید اتفاق میافتد و واکنش از طریق یک حالت گذار باز انجام میشود.
Sodium borohydride
Sodium borohydride, also known as sodium tetrahydridoborate and sodium tetrahydroborate is an inorganic compound with the formula NaBH. This white solid, usually encountered as a powder, is a reducing agent that finds application in chemistry, both in the laboratory and on an industrial scale. It has been tested as pretreatment for pulping of wood, but is too costly to be commercialized. (516) The compound is soluble in alcohols, certain ethers, and water, although it slowly hydrolyzes." The compound was discovered in the 1940s by H. I. Schlesinger, who led a team seeking volatile uranium compounds. Results of this wartime research were declassified and published in 1953.
NaBH4 reduces many organic carbonyls, depending on the precise conditions. Most typically, it is used in the laboratory for converting ketones and aldehydes to alcohols. It efficiently reduces acyl chlorides, anhydrides, α-hydroxylactones, thioesters, and imines at room temperature or below. It reduces esters slowly and inefficiently with excess reagent and/or elevated temperatures, while carboxylic acids and amides are not reduced at all . NaBH4 reacts with water and alcohols, with evolution of hydrogen gas and formation of the corresponding borate, the reaction being especially fast at low pH.
Nevertheless, an alcohol, often methanol or ethanol, is generally the solvent of choice for sodium borohydride reductions of ketones and aldehydes. The mechanism of ketone and aldehyde reduction has been scrutinized by kinetic studies, and contrary to popular depictions in textbooks, the mechanism does not involve a 4-membered transition state like alkene hydroboration,[19] or a six-membered transition state involving a molecule of the alcohol solvent.[20] Hydrogen-bonding activation is required, as no reduction occurs in an aprotic solvent like diglyme. However, the rate order in alcohol is 1.5, while carbonyl compound and borohydride are both first order, suggesting a mechanism more complex than one involving a six-membered transition state that includes only a single alcohol molecule. It was suggested that the simultaneous activation of the carbonyl compound and borohydride occurs, via interaction with the alcohol and alkoxide ion, respectively, and that the reaction proceeds through an open transition stat
Chemical formula NaBH4
Molar mass 37.83 g/mol
Appearance white crystals
hygroscopic
Density 1.07 g/cm3
Melting point 400 °C (752 °F; 673 K)(decomposes)[1]
Solubility in water 550 g/
Solubility soluble in liquid ammonia, amines, pyridine
سدیم بورهیدرید مرک کد 818823
نام ماده : Sodium borohydride
cas نامبر: 16940-66-2
فرمول خطی: H₄BNa
فروش در پکیجهای 25 گرمی و 100 گرمی
سدیم بورهیدرید مرک کد 106371
نام ماده : Sodium borohydride for analysis 106371
cas نامبر: 16940-66-2
فرمول خطی: H₄BNa
فروش در پکیجهای 100 گرمی
سدیم بورهیدرید مرک کد 806373
نام ماده : Sodium borohydride
cas نامبر: 16940-66-2
فرمول خطی: H₄BNa
فروش در پکیجهای 10 – 25 – 100 – 500 گرمی (گرانولی)
درباره ما
شركت مينا تجهيز آريا با سالها تجربه و با استفاده از تخصص،تعهد، تجربه و دانش هاي نوين اقدام به تهيه، توزيع مواد شیمیایی ( آزمایشگاهی ، صنعتی ) و تجهيز لوازم آزمايشگاهي، شيشه آلات و كليه ملزومات آزمايشگاهي از شركت هاي داخل و خارج كشور نموده است.
برای پرسش و پاسخ و دریافت قیمت و موجودی با کلیک روی لینک زیر به تلگرام شرکت پیام دهید
آدرس : تهران - میدان توحید- خیابان امیر لو(نبش کوچه خودرو) - پلاک 42- طبقه دوم - واحد5
ایمیل : minatajhiz_aria@yahoo.com
شماره ها تماس : 02166901187 - 02166900058
شماره های همراه :09362048289 - 09927282910
شماره های واتس آپ ، ایتا ، تلگرام و روبیکا : 09927282910

